Tag: safety
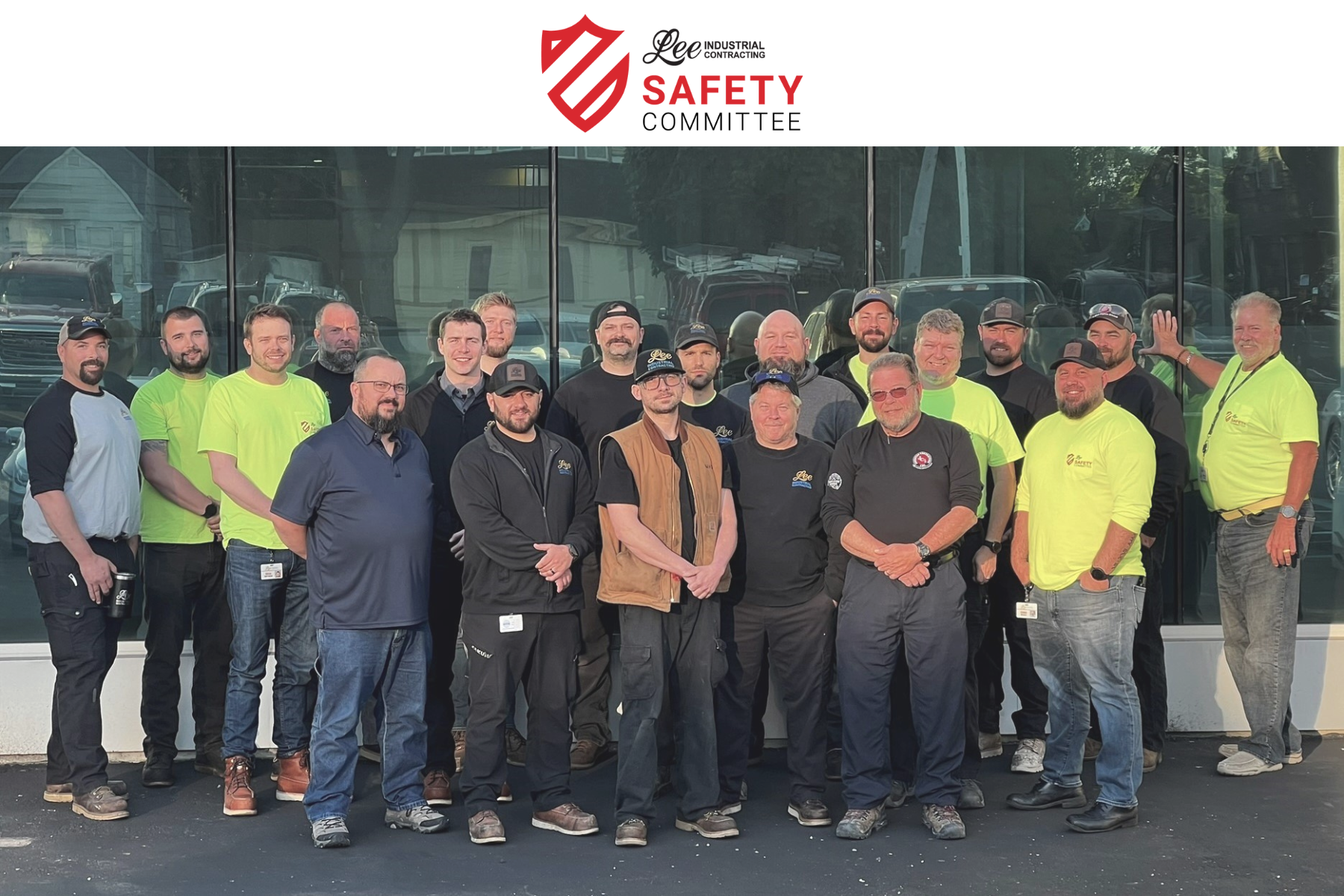

In today’s workplace, prioritizing employee safety and well-being is essential. At Lee, where employees are owners, safety is not merely a directive from management; it is a collective responsibility that is fundamental to our organization.
As part of our proactive approach to safety, Lee has established a Safety Committee that plays a pivotal role in maintaining a secure work environment. Working alongside the Safety Department and management, the Safety Committee acts as a conduit for raising concerns, offering suggestions for risk mitigation, and setting an example for other employees.
Here’s how the Safety Committee is instrumental in fostering a culture of safety at Lee:
- Enhanced Communication: The Safety Committee facilitates open communication channels between employees, the Safety Department, and management. By serving as a liaison, it ensures that concerns, suggestions, and feedback regarding safety are effectively communicated and addressed.
- Risk Mitigation: Through regular meetings and discussions, the Safety Committee collaborates with the Safety Department and management to identify potential workplace risks and hazards. By sharing insights and observations, they contribute to the development of proactive measures to mitigate these risks and enhance overall safety.
- Employee Engagement: Members of the Safety Committee actively engage with their peers to promote safety awareness and best practices. By representing their colleagues and demonstrating a commitment to safety through their actions, they inspire others to prioritize safety in their daily tasks and interactions.
- Continuous Improvement: The Safety Committee plays a pivotal role in driving continuous improvement in safety protocols and procedures. Through regular review and evaluation of current practices, it identifies areas for enhancement and collaborates closely with the Safety Department and management to implement necessary changes.
- Empowerment: By empowering employees to voice their concerns and suggestions through the Safety Committee, Lee fosters a sense of ownership and accountability for safety among its workforce. This empowerment not only strengthens employee morale but also leads to a more proactive approach to safety throughout the organization.
Our Safety Committee here at Lee plays a vital role in promoting a culture of safety, collaboration, and continuous improvement. By working alongside the Safety Department/Management, it ensures that safety remains a top priority and that every employee owner is actively involved in maintaining a secure and healthy work environment.
Subscribe and receive updates via email
Every year OSHA releases the top 10 most cited violations list to inform the industry of what safety topics to focus on in future trainings as well as on job sites. Recently OSHA released their preliminary top 10 most cited violations list for 2019. The 2019 list includes the same violations as 2018.
These ratings and violations do not include violations found by state enforcement agencies yet reflect nationwide safety issues that need to be amended.
Below is the list of OSHA’s 2019 top 10 citied violations:
- Fall Protection – General Requirements – 7,014 Total Violations
- Hazard Communication – 4,170 Total Violations
- Scaffolding- 3,228 Total Violations
- Lockout/Tagout – 2,975 Total Violations
- Respiratory Protection – 2,826 Total Violations
- Ladders – 2,766 Total Violations
- Powered Industrial Trucks – 2,347 Total Violations
- Fall Protection – Training Requirements 2,059 Total Violations
- Machine Guarding – 1,987 Total Violations
- Personal Protective & Life Saving Equipment – Eye & Face Protection 1,630 Total Violations
Our client success teams include customer-centric account managers, project managers and safety personnel. This team works exclusively with their clients to ensure that both the clients’ and Lee Contracting’s safety policies are enforced. The success of this union results in our safety representatives becoming experts in their customers’ exact safety policy. Between our safety policies and our customers’ safety policies, we encompass all areas, recognizing and preventing any possible hazards.

At Lee Contracting, we don’t just talk about safety, we put safety into action. We continuously train our employees to recognize unsafe working conditions to minimize risk and the potential for injury. Our commitment to safety and health is designed to prevent employee accident/injury while promoting a positive environment. When our company meets our safety goals, it translates to better service and reduced costs for all our customers. Learn more about our safety program on our website today.
Call us today to receive a free quote on your next industrial project (888) 833-8776.
Subscribe and receive updates via email
Forklift accidents are often responsible for creating costly delays, potential lawsuits and stressful work environments. However, the human cost of forklift misuse is far greater. An estimated 85 people die annually from forklift accidents, according to OSHA statistics. Overall, nearly 100,000 workers are injured per year as a result of forklift misuse.
Nearly 35,000 serious forklift accidents happen annually according to OSHA. Almost half of those accidents take place in manufacturing facilities. Construction, warehouses and transportation also see their share of forklift collisions. Some accidents are due to driver error. Inadequate training and poor forklift safety design also cause mishaps and injuries. Here’s everything you need to know about forklift accidents and how to keep yourself and other employees safe in the workplace.
Types of Forklift Accidents
Accidents vary according to the kind of forklift and the work the forklift and driver are performing. Some forklift hazards are:
- Driving off a loading dock
- Falls between loading docks and trailers
- Falls from lift tines or elevated pallets
- Collisions with pedestrians
Why are Forklifts Dangerous?
Forklifts can be dangerous if used improperly. Forklifts are heavier in the rear to compensate for the heavy loads being carried in the front. This uneven weight distribution can make a forklift difficult to handle. Other reasons forklifts can be a dangerous piece of equipment:

- Forklifts can weigh up to 9,000 pounds
- Forklifts can travel up to 18mph
- Forklifts only have front brakes, making them harder to stop
- Forklifts are often used to raise hefty loads to considerable heights, a dangerous combination
HOW TO IMPROVE FORKLIFT SAFETY
Improve Housekeeping
Maintaining a clean jobsite will allow for safer use of all equipment including forklifts. Keep the floor/ground clear of debris, move large equipment, trash, workers’ personal items and any other potential hazards out of the forklift’s route. Narrow aisles, excessive dust and raised platforms are common workplace design problems that need to be kept in mind while planning a forklift route.
AVOID DANGEROUS BEHAVIORS WITH TRAINING
OSHA has found that nearly 70 percent of all forklift accidents could have been avoided by following correct training and policy. Human error is a common culprit behind forklift accidents. Adequate operator training is key in avoiding accidents. Forklift operators can accidentally drive forklifts off loading docks, carry unstable loads and tip over and strike a fellow employee around a blind corner, just to name a few potentially deadly circumstances.
Safe practices for drivers include:
- Loading the forklift so that operator visibility is not impaired
- Ensuring fellow workers in the area know there is an operating forklift nearby
- Avoiding excessive speeds
- Taking extra caution when coming around blind corners, doorways and other areas of high foot traffic
Employees who are not involved in forklift duties still have a responsibility to keep themselves out of harm’s way. Here are some safety tips:
- Keep a safe distance from the forklift at all times
- Make eye contact with the driver if approaching a moving forklift
- Do not walk under raised forks

IMPLEMENT A SAFETY PLAN
Having a forklift safety program at your business helps keep your employees safe. The recommended forklift safety program includes regular vehicle check-ups and making sure that the equipment is only used for its intended purpose. Proper use of equipment is crucial to prevent accidents and ensure that your workspace remains safe. Taking the time to examine forklifts and determine that each forklift is up-to-date on breaking mechanisms, warning lights and mechanical features is paramount to keeping your workers safe. Using the proper equipment for the task at hand is key to keeping your workplace accident free. There are a variety of different forklifts for different needs, and it is key to use the right lift for the right task.
At Lee Contracting, the safety of our personnel is top priority. Learn more about our safety department and how we stay safe.
Call us today to receive your free quote (888) 833-8776 or visit our website.
Subscribe and receive updates via email

According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the rate of worker deaths and reported injuries in the United States has decreased by more than 60 percent in the past four decades since the Occupational Safety and Health Act was passed. However, every year, more than 5,000 workers are killed on the job (a rate of 14 per day), and more than 3.6 million suffer a serious job-related injury or illness.
Serious job-related injuries or illnesses don’t just hurt workers and their families but can hurt business in a variety of ways. Implementing a safety and health program, however, can improve small- and medium-sized businesses’ safety and health performance, save money, and improve competitiveness.
Safety and health programs help businesses:
- Prevent workplace injuries and illnesses
- Improve compliance with laws and regulations
- Reduce costs, including significant reductions in workers’ compensation premiums
- Engage workers
- Enhance social responsibility goals
- Increase productivity and enhance overall business operations
Lee Contracting is participating in this year’s Safe & Sound week by holding many trainings lead by our own safety staff and external safety companies. These trainings include:
- Mobile Crane Training
- Lockout Tagout
- Hydration Heat Stress
- First Aid & CPR
- Hand & Eye Protection
- Ladder Safety

We also participated in a community event hosted by the Construction Association of Michigan. During the event, we learned the core elements of a safety and health management system. We also received resources to keep our safety program up to date to ensure the safety of our staff.
At Lee Contracting, we are committed to safety. With continuous training and our dedicated safety staff, we provide world-class safety on all our jobs.
You can learn more about Safe & Sound Week here.
Receive your free quote today or call us today at (888) 833-8776 to learn how we can safely complete your next industrial project.
Subscribe and receive updates via email
Most chemicals are harmless but chronic illnesses can stem from exposure to certain chemicals. In our new hire training we cover the major OSHA concerns of asbestos, lead and silica, but what about the chemicals we deal with every day? Sealants, adhesives, paints and cleaners can all be sources of hazards. With the new Globally Harmonized System (GHS) it is easier to be aware of what hazards are involved with every chemical.
Just like chemical gases, even though you don’t see any harm, dangers still exist. Therefore, it is critically important to look at the packaging of chemicals for symbols that annotate what dangers are present. On a common Silicone Dissolver, the symbols below will appear on the packaging. They stand for hazards regarding skin corrosion/irritation, single exposure organ toxicity, aspiration toxicity and flammable liquids.

At Lee Contracting we utilize Safety Data Sheets (SDS) to inform on-site personnel of hazardous chemicals and how to safely work with them. On the SDS, the appropriate PPE and engineering controls can be found. Also on the SDS, you can find the permissible exposure limit (PEL) and time-weighted average (TWA) to know when a respirator is required or when to change workers.
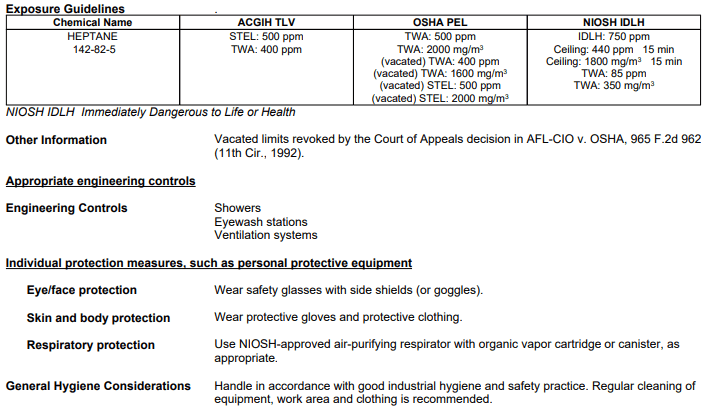
Additional safety tips when working with hazardous materials include:
- Use non-toxic, non-flammable products whenever possible.
- When handling hazardous materials:
- Use the chemical only as directed.
- Use personal protective equipment as recommended by manufacturers and required by your employer. These could include protective clothing, rubber gloves, goggles and face shields.
- Be sure you are working in an adequately ventilated area with approved fire protection.
- Do not perform hot work where flammable chemicals are used or stored.
- Check that first aid is readily available.
- Store chemicals in a properly ventilated, locked area and post warning signs.
Our skilled tradespeople are trained since day one to put safety first. We pride ourselves on getting all employees home safe. Learn more about our safety department today.
Receive your free quote today by calling (888) 833-8776 or filling out our web form.
Subscribe and receive updates via email
This week is 2019 Trench Safety Stand Down Week. OSHA is supporting this event, which is sponsored by the National Utility Contractors Association (NUCA), the North American Excavation Shoring Association (NAXSA), the Trench Shoring and Shielding Association (TSSA) and the National Association of Home Builders (NAHB).
Excavation and trenching continue to be some of the most dangerous construction activities. There have been five excavation fatalities in Michigan between 2013 and 2017. For each fatal incident, there are dozens of excavation accidents resulting in serious injuries.
When done safely, trenching operations can reduce worker exposure to cave-ins, falling loads, hazardous atmospheres and hazards from mobile equipment. OSHA standards require that trenches and protective systems be inspected daily and as conditions change by a competent person before work begins.

Never enter a trench unless:
- It has been properly inspected by a competent person.
- Cave-in protection measures are in place.
- There is a safe way to enter and exit.
- Equipment and materials are way from the edge.
- It is free of standing water and atmospheric hazards.
Prevent trench collapses:
- Trenches 5 feet deep or greater require a protective system.
- Trenches 20 feet deep or greater require a protective system designed by a registered professional engineer.
Protective systems for trenches:
- SLOPE or bench trench walls by cutting back the trench wall at an angle inclined away from the excavation.
- SHORE trench walls by installing aluminum hydraulic or other types of supports to prevent soil movement.
- SHIELD trench walls by using trench boxes or other types of supports to prevent soil cave-ins.
Lee Contracting continues our commitment to safety by participating in this important safety stand down week. Many foundations department members and safety representatives attended the CAMTEC (Construction Association of Michigan Training and Education Center) excavation, trenching and shoring class. All our on-site crews participated in a weekly toolbox talk to be aware of and eliminate excavation and trenching hazards.
Contact us today or call us at (888) 833-8776 to learn how Lee Contracting can benefit your next project.
Subscribe and receive updates via email

Driving is something that we all do for our job, whether commuting to the office or driving to a job site. With an average of 6 million car accidents each day throughout the United States, we do not expect to be entirely exempt. According to auto insurance industry experts, the average driver will be in a car accident once every 18 years or so. This means that over the course of a drivers lifetime, they will be in about 4 car accidents.
Be aware of your surroundings. On the road or on the job site, be aware of your surroundings and those around you. Never assume that others see you. Drive defensively, check your blind spots and use your turn signals at the appropriate time before moving over to let those around you know of your intentions.
Use your lights. Many drivers only turn their lights on at night. However, on a foggy, rainy, or snowy day, your lights make you more visible to others as well as increase your visibility. Even if you think, “Well, I can see fine,” turn your lights on anyway. It will be beneficial for you and the other drivers on the road.
Get over. In February, Michigan expanded the move over law which mandates that motorists slow down by 10 mph below the posted speed limit and when possible, move over a lane when passing a police or emergency vehicle on the side of the road. Over a dozen Michigan Police Officers have been struck by vehicles on the side of the road since January. Failure to get over could not only result in a $400 ticket but also puts other lives at risk.
Don’t drive distracted. Every day, about every 9 people are killed and more than 1,000 people are injured from an accident involving a distracted driver. Phone use is a major distraction from driving. On average, it takes most people 5 seconds to take their eyes off the road to read or send a text. At 55 mph, that equates to driving the full length of a football field with your eyes closed. Most phones now have a ‘Driving Mode’ that disables notifications from becoming a distraction while driving.

At Lee, all drivers are taught general safe operating procedures and safe procedures applicable to their individual vehicles. From the start of the day to the end, safety is our focus.
Schedule your conversation with us by calling (888) 833-8776 or fill out our online form.
Subscribe and receive updates via email
In 2018 “struck by” was the leading cause of worker fatalities in Michigan. As of today, “struck by” accounts for 5 of the 7 Michigan worker fatalities in 2019.
Common struck by hazards in construction:
- Struck by flying object: Flying object hazards exist when something has been thrown, hurled or propelled. It can include instances when a piece of material separates from a tool, machine or other equipment, striking a worker resulting in injury or fatality. A hazard also exists if an object is ejected under power by a tool or equipment usually designed for that purpose such as a nail from a nail gun. Powder-actuated tools are particularly hazardous due to the force behind the fastener. These fasteners are designed to go through wood, concrete and steel which means they can certainly go through a worker.
- Struck by falling object: When the source of injury is falling from an elevation to a lower level, including instances where the injured person is crushed, pinned or caught under a falling object, other than collapsing material or structures, resulting from being struck by a falling object or equipment.
- Struck by swinging object: When materials are mechanically lifted, they have the potential to swing and strike workers. As the load is lifted, the materials may swing, twist or turn. This movement can catch workers by surprise and they could be hit by the swinging load. Windy conditions are especially hazardous because the load will swing more. Depending on where the worker is standing and the force behind the load, the worker may fall to another level after being struck and sustain even greater injuries. In addition to swinging, loads can slip from their riggings and strike workers. Loads must be rigged properly to prevent slippage.
- Struck by rolling object: When an object which is rolling, moving or sliding on the same level at which the worker is located. Includes instances in which the worker is struck or run over by a moving vehicle without being caught under it or instances in which the worker is struck by a sliding object or equipment on the same level.
Awareness of your surroundings and proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) can go a long way in avoiding injuries at a construction site. It is important to alert all workers of areas where there is greater potential for struck-by accidents to occur and to limit employee access to those areas.

Protection against struck by hazards:
- Stay away from heavy equipment when it is operating
- Wear high-visibility reflective clothing and all required PPE
- Do not use tools with loose, cracked or splintered handles
- Secure all tools and materials
- Be sure to be trained on safe operation of machinery
- Keep work areas clear
At Lee Contracting, we use mobile and overhead cranes daily. Our employees never walk underneath any suspended loads, always wear a hard hat while in the presence of overhead work and are always aware of their surroundings. If we ever perform unusual work or work outside the normal scope on a project, our Safety Department will survey the work area with the Project Manager and an Owner’s representative as necessary, to determine any special hazards or exposures.
We are proud to have the opportunity to continue serving our customers locally and nationwide. Learn more about our safety culture today.
Schedule your conversation with us by calling (888) 833-8776 or fill out our online form.
Subscribe and receive updates via email
Many safety hazards are present when performing hot work including burns, eye damage, electrical shock, cuts and crushed toes and fingers. Many of these can be controlled with proper work practices and personal protective equipment (PPE). The PPE required for most hot work includes:
- Helmet or goggles to protect eyes and face from radiation, debris, sparks and intense light.
- Flame resistant clothing and apron to protect exposed skin from heat, fires and burns.
- Ear plugs to protect ears from noise.
- Boots and gloves to protect feet and hands from heat, burns, fires and electric shock.
The potential for starting a fire is among the most significant risks of hot work. An essential member of some hot work teams is the “fire watch.” Fire watch personnel should be trained and aware of the following:
- Proper use and placement of a fire extinguisher.
- Recognition of fire hazards such as combustible and/or flammable materials and chemicals.
- Plant emergency notification and procedures.
- Only qualified personnel will perform welding, cutting and brazing operations.
- All welding and burning equipment will be inspected prior to use.
- Hot Work Permits will be used when required by the Owner or when hazards warrant as determined by a qualified person.
- Any welding, cutting or burning of products containing lead, cadmium, zinc, mercury, beryllium or other exotic metals or paints require ventilation or respirators.
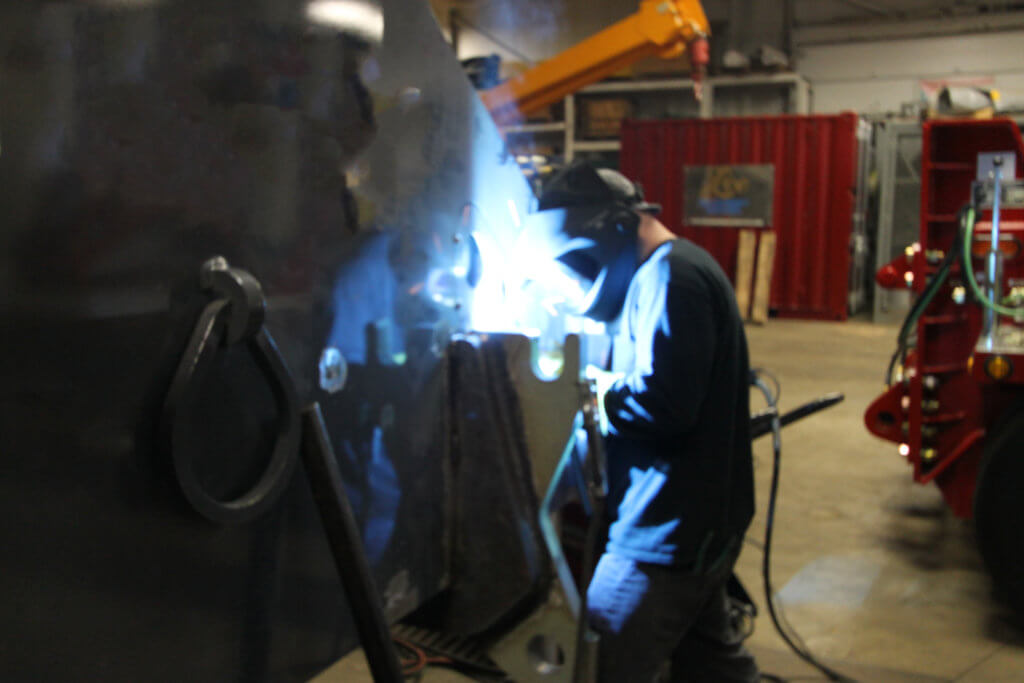

The best option when completing hot work is to remove all hazards. In some situations, hazards cannot be removed. If hazards cannot be removed all precautions must be taken to confine heat and sparks. If certain hazards cannot be protected all hot work activity should be relocated.
At Lee Contracting, the safety of our personnel is top priority. Learn more about our safety department and how we stay safe.
Call us today to receive your free quote (888) 833-8776 or visit our website.
Subscribe and receive updates via email

Aerial lifts are vehicle-mounted, boom-supported aerial platforms, such as scissor lists or bucket trucks, used to access utility lines and other above ground job sites. The major causes of fatalities are falls, electrocutions, and collapses or tip overs. Employers must take measurements to ensure the safe use of aerial lifts. At Lee Contracting, our employees are trained from day one to ensure safety on all job sites.
Lee Contracting’s aerial lift safety procedure includes:
• Aerial lifts may be “field modified” for uses other than those intended by the manufacturer provided the modification has been certified in writing by the manufacturer or by an equivalent entity.
• Lift controls shall be tested each day prior to use to determine that such controls are in safe working conditions. Tests shall be made at the beginning of each shift during which the equipment is to be used to determine that the brakes and operating systems are in proper working condition.
• Only authorized persons shall operate an aerial lift and boom and basket load limits specified by the manufacturer shall not be exceeded.
• Aerial lifts shall have a working back-up alarm audible above the surrounding noise level or the vehicle is back up only when an observer (spotter) signals that it is safe to do so.
• The minimum clearance between electrical lines and any part of the equipment (i.e. crane or load) shall be 20 feet for lines rated 50 kV or below.
• Employees shall always stand firmly on the floor of the basket and shall not sit or climb on the edge of the basket or use planks, ladders, or other devices for a work position.
• An approved fall restraint system shall be worn when working from an aerial lift. The fall restraint system must be attached to the boom or basket. An approved fall restraint system shall be attached to the boom or basket when working from an aerial lift and it is not permitted to be attached to adjacent poles or structures.
• All employees who operate an aerial lift device shall be trained in the safe operation of the specific device they will operate. Training must conform to all OSHA requirements.
Safe aerial lift operation requirements per OSHA:
• Complete the required training prior to operating any equipment.
• Be aware of and remove any hazards, including overhead hazards.
• Prior to each work shift, conduct a pre-start inspection to ensure safe use of the equipment.
• Prior to each work shift, conduct a work zone inspection to assure the area is eliminated of all hazards.
• Follow all fall protection requirements learned in training.
• Always confirm stability of the work zone by using outriggers, brakes, chocks, along with cones and signs to warn others.
Our skilled tradespeople are trained since day one to put safety first. We pride ourselves on safe operation of all equipment and getting all employees home safe. Learn more about our safety department today.
Receive your free quote today by calling (888) 833-8776 or filling out our web form.


